Comparing the Performance of Apps with Databases Between TCP and Unix Sockets

Normally, when using a database for small-scale tasks in a container, we usually connect via TCP/IP, right? But did you know that you can easily improve performance by removing the TCP overhead by using Unix sockets instead? Let’s see what the results are.
docker-compose.yml
Let’s start by spinning up a database in Docker using Docker Compose, keeping it as default as possible, as shown below:
x-default: &deafult-env
TZ: Asia/Bangkok
x-mariadb: &mariadb-env
MARIADB_ALLOW_EMPTY_ROOT_PASSWORD: true
MARIADB_AUTO_UPGRADE: true
services:
mariadb:
image: mariadb:lts
environment:
<<: [*deafult-env, *mariadb-env]
volumes:
- mariadb_data:/var/lib/mysql
- ./tmp/run:/run/mysqld
ports:
- 3306:3306
redis:
image: redis:alpine
environment:
<<: [*deafult-env]
volumes:
- redis_data:/data
- ./tmp/run:/data/run
command: [
"redis-server",
"--unixsocket /data/run/redis.sock",
]
ports:
- 6379:6379
volumes:
mariadb_data:
redis_data:
After docker compose up -d, it will look something like this:
Redis
Let’s start with the fastest and simplest database in the example. We will test read and write operations.
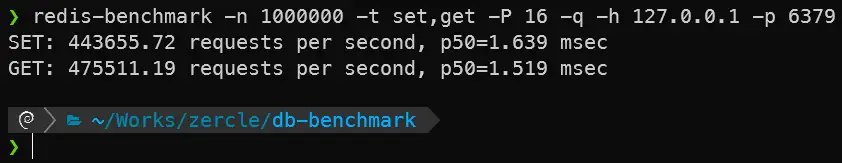
TCP/IP
redis-benchmark -n 1000000 -t set,get -P 16 -q -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6379
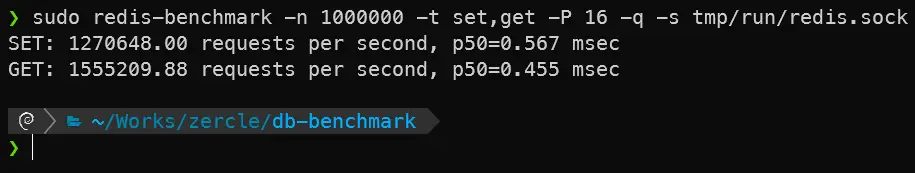
UNIX socket
redis-benchmark -n 1000000 -t set,get -P 16 -q -s tmp/run/redis.sock
MariaDB
Next, let’s test a popular database. We will test read and write operations as before.
Prepare data for testing
First, create a database and table for sysbench.
sysbench oltp_read_write --db-driver=mysql --mysql-host=127.0.0.1 --mysql-user=root --mysql-db=sysbenchtest --threads=16 prepare
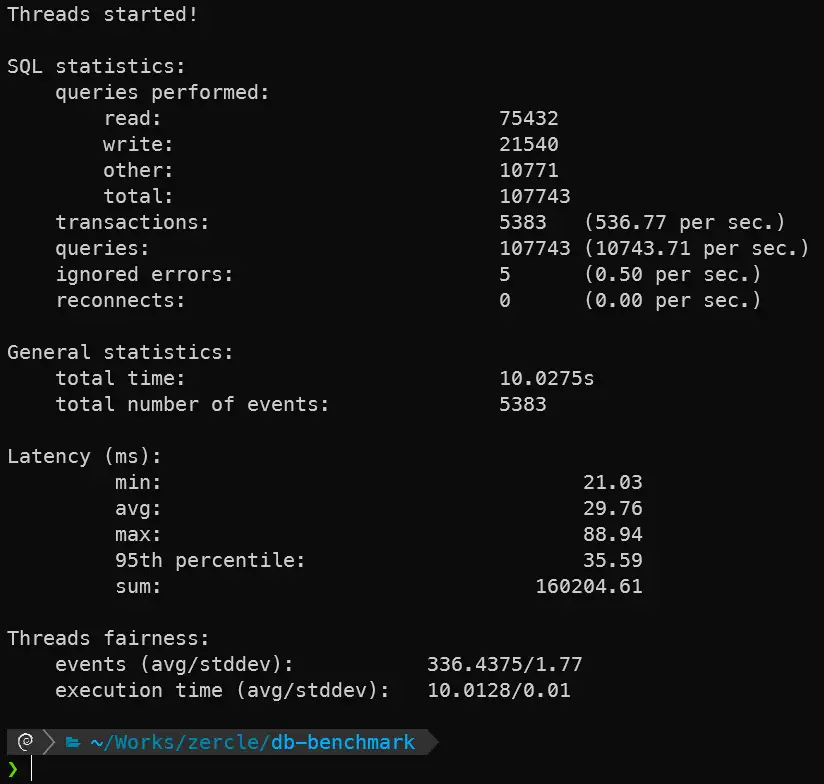
TCP/IP
sysbench oltp_read_write --db-driver=mysql --mysql-host=127.0.0.1 --mysql-user=root --mysql-db=sysbenchtest --threads=16 run
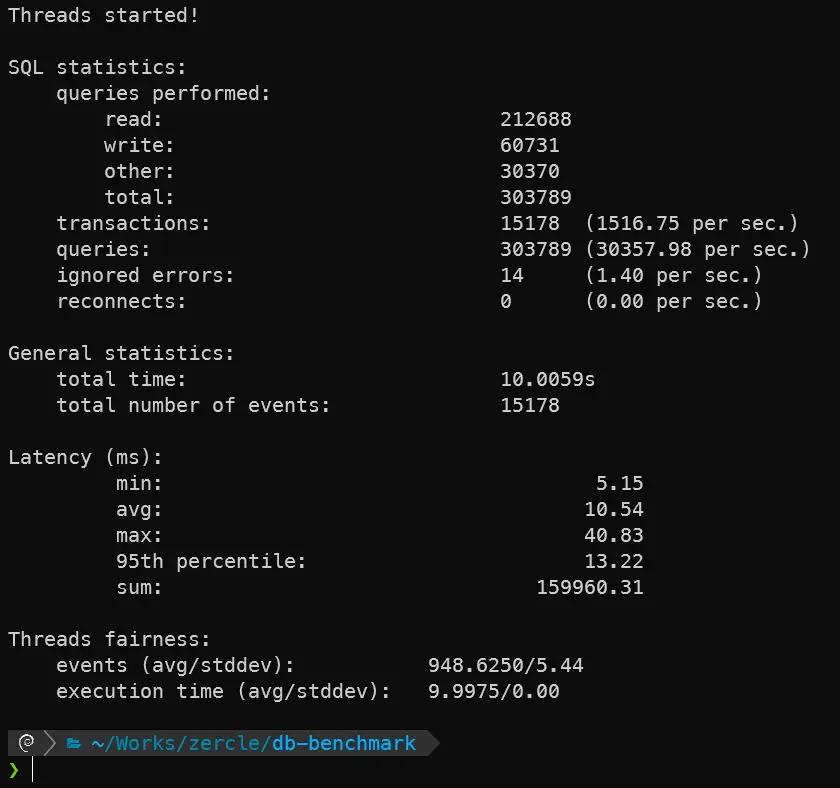
UNIX socket
sysbench oltp_read_write --db-driver=mysql --mysql-socket=tmp/run/mysqld.sock --mysql-user=root --mysql-db=sysbenchtest --threads=16 run
Conclusion
| read (req/s) | write (req/s) | latency avg (ms) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Redis TCP | 475,511.19 | 443,655.72 | 1.519 / 1.639 |
| Redis UnixSocket | 1,555,209.88 | 1,270,648.00 | 0.455 / 0.567 |
| MariaDB TCP | 75,432 | 21,540 | 29.76 |
| MariaDB UnixSocket | 212,688 | 60,731 | 10.54 |
As you can see, by reducing the overhead of TCP and using Unix sockets instead, we can handle a much higher load without having to significantly scale up our resources. Or, in Kubernetes workloads with sidecars, you can use Unix sockets for inter-process communication instead of TCP/IP.
Note: This only works on nodes that share the same volume.